How do Transformer LMs filter from a list?
We investigate how LLMs perform filtering operation such as find the fruit in a list. Turns out, they use surprisingly elegant mechanisms similar to how a programmer might write filter functions in code.
We find that LLMs implement a neural analogue of filtering operations using specialized
attention heads
that we call filter heads. These
heads encode the filtering criterion (the predicate) in their query states of
certain
tokens. This encoding is sufficiently abstract that it can be transported to a different context
to trigger the execution of the same filtering operation on a new list of candidates, presented
in a different format/language, even in a
different task.
Filter Heads
Try hovering over the tokens below! When prompted with filtering tasks, a set of attention heads focus their attention on the correct item in the list. This behavior is consistent across a range of different prompts and tasks.
The panel shows aggregated attention scores of a set of filter heads in Llama-70B from the last token.
Portability
These filter heads capture an abstract representation of the filtering criterion (the
predicate) in their query states at certain token positions. This encoding can be
transported to a different context to trigger the execution of the same filtering operation on a new
list of candidates. This suggests that LLMs can implement abstract rules that can be reused in
different
situations.
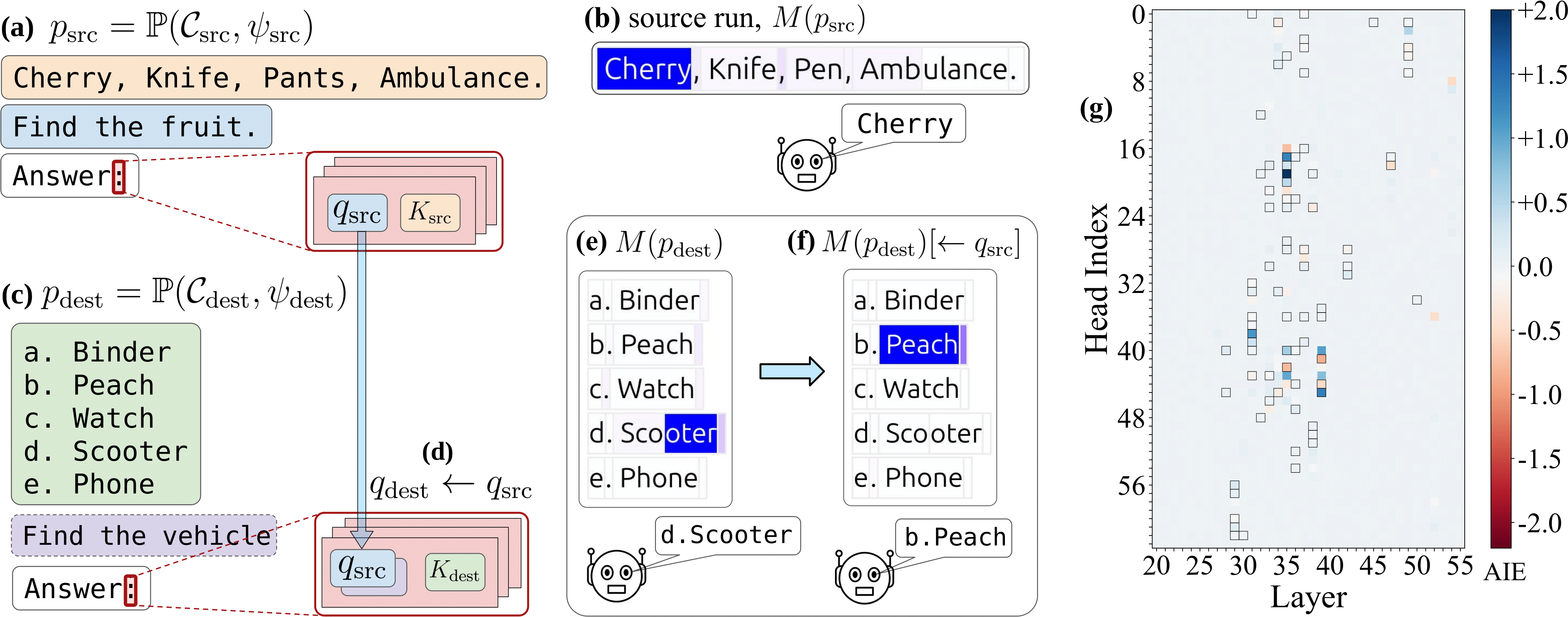
":".
(b) The head focuses its attention on the one fruit in the list.
(c) We examine the same attention head's behavior in a second prompt
pdest searching a different list for a vehicle.
(d) and we also examine the behavior of the head when patching its query state
to use the qsrc vector from the source context.
(e) The head attends to the vehicle but then
(f) redirects its attention to the fruit in the new list after the query vector
is patched.
(g) A sparse set of attention heads work together to conduct filtering over a
wide range of predicates. These filter heads are concentrated in the middle layers (out of 80
layers in Llama-70B).
"Peach" (or
whatever the task format is). In formal notation, the causality score is defined as:
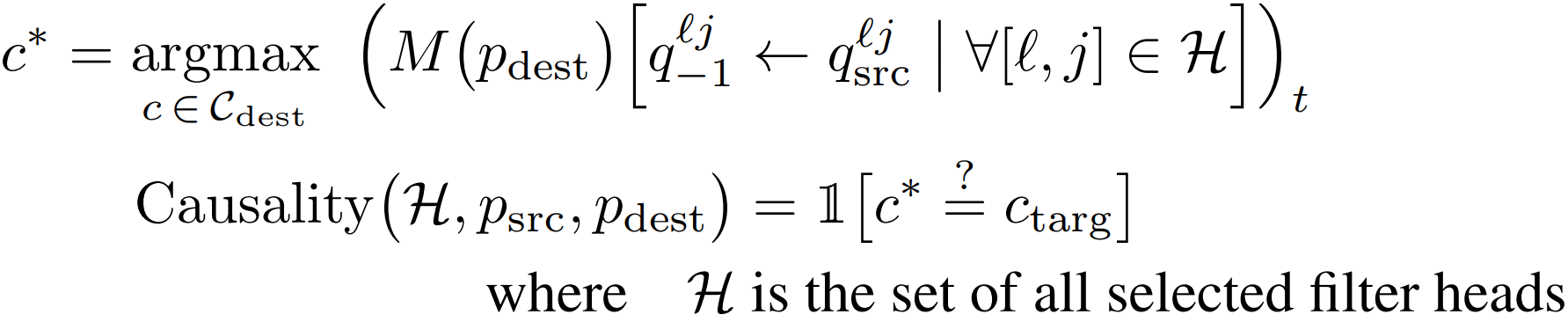
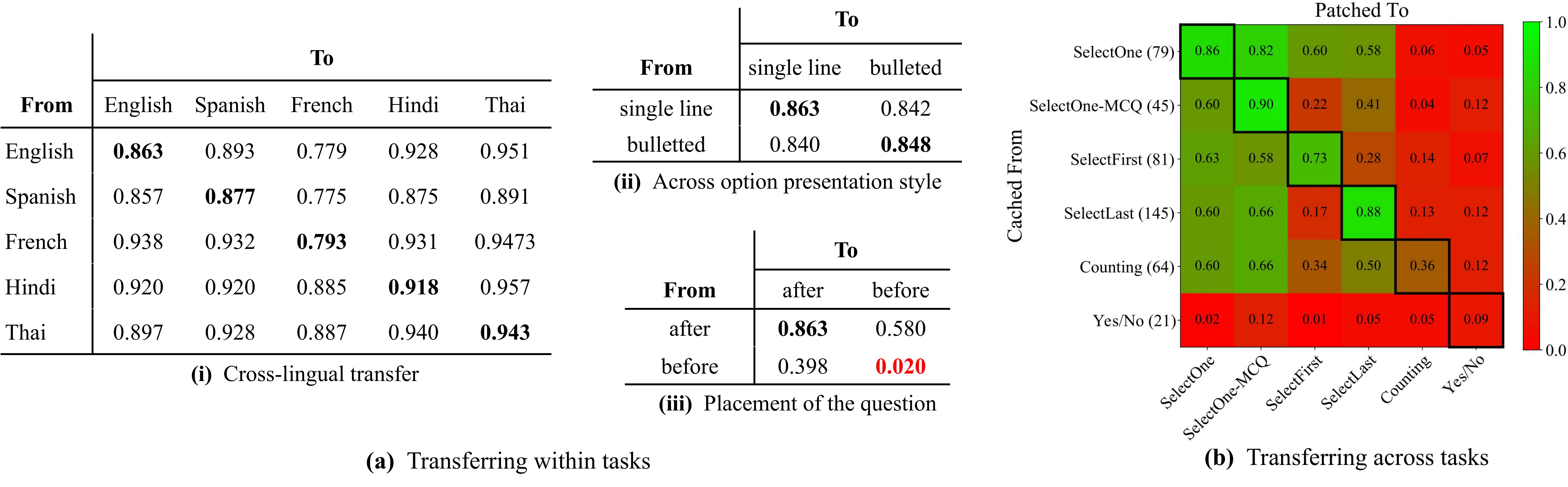
We also check predicate portability across tasks with a suite of six tasks that require a different reduce step after the filtering. We observe non-trivial portability for a group of similar tasks, suggesting that a range of different tasks can share the same filtering sub-circuit.
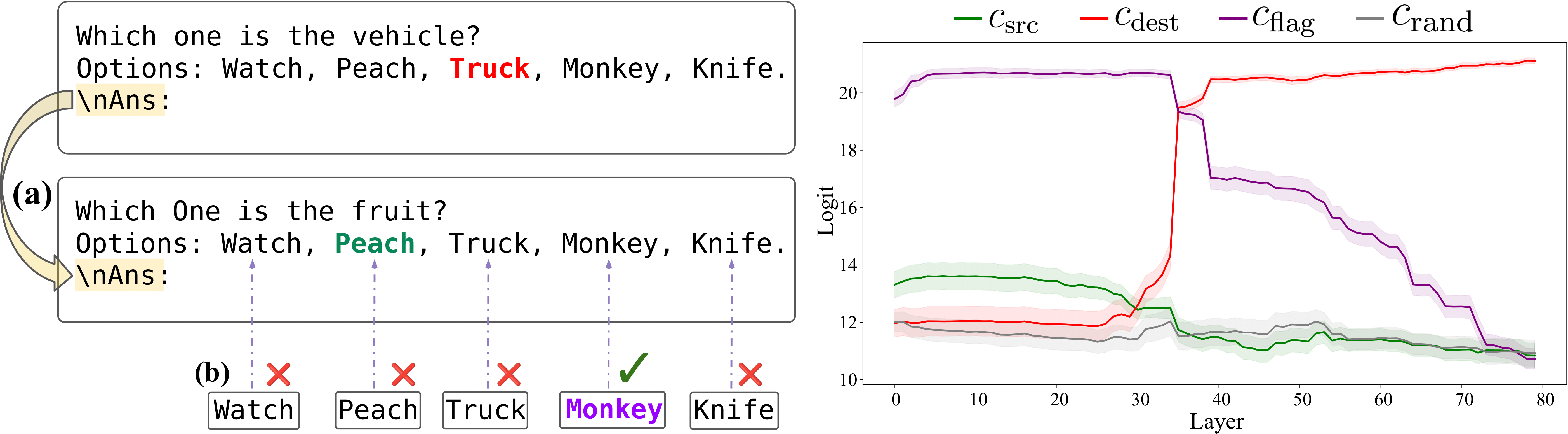
Two ways to perform filtering: Lazy vs Eager
In the prompt if the question is presented before the list of options, we notice that the causal influence of the filter heads drops to near zero! We investigate this further and find that this seemingly trivial change can fundamentally alter the computation implemented by the LM. When the question is presented before, the LM knows what to look for upfront. So it can eagerly evaluate each item in the list, as they are presented, and store a "flag" in their latents, indicating whether the item satisfies the predicate or not.We validate this flag-based eager evaluation hypothesis with a series of carefully designed causal mediation analyses. If we swap this flag with another item in the list, in the question-before context the LM consistently picks the item carrying the flag, while the query-after prompt doesn't show any sensitivity to this intervention. Checkout our paper for full details!
Application
We can leverage the distinctive attention pattern of the filter heads in practical applications. One cool example: detecting false information in a free form text. The setup is simple: we break text into lines, append"Which of the above statements are false?\nAnswer:", and
monitor where the filter heads look from the last token position. They consistently zero in on the
last
tokens of the false statements, which makes sense as the LM needs to read the entire
statement
to determine its veracity.
False Information Detection
💡 Key Takeaways
- LLM can implement filter operations with specialized filter heads that encode abstract filtering rules.
- These rules are portable and generalizable - they transfer across formats, languages, and related tasks.
- LLMs use two different strategies (lazy vs. eager evaluation) depending on what information is available.
Related works
 Nikhil Prakash, Natalie Shapira, Arnab Sen Sharma, Christoph Riedl, Yonatan Belinkov, Tamar Rott
Shaham, David Bau, Atticus Geiger
Language Models use Lookbacks to Track Beliefs 2025.
Nikhil Prakash, Natalie Shapira, Arnab Sen Sharma, Christoph Riedl, Yonatan Belinkov, Tamar Rott
Shaham, David Bau, Atticus Geiger
Language Models use Lookbacks to Track Beliefs 2025.
Notes: LMs use a mechanism similar to the double pointers (**) in C++ to track relationships
between entities in theory-of-mind reasoning tasks.
 Eric Todd, Millicent L. Li, Arnab Sen Sharma, Aaron Mueller, Byron C. Wallace, David Bau.
Function Vectors in Large Language Models 2024.
Eric Todd, Millicent L. Li, Arnab Sen Sharma, Aaron Mueller, Byron C. Wallace, David Bau.
Function Vectors in Large Language Models 2024.
Notes: LLMs encode the functional transformations demonstrated with ICL examples as compact
representations in their latent space.
Citation
This work is under review. The preprint can be cited as follows.
bibliography
Arnab Sen Sharma, Giordano Rogers, Natalie Shapira, and David Bau. "LLMs Process Lists With General Filter Heads" (2025). arXiv preprint.
bibtex
@article{sensharma2023filter,
title={LLMs Process Lists With General Filter Heads},
author={Arnab Sen Sharma and Giordano Rogers and Natalie Shapira and David Bau},
year={2025},
eprint={2510.26784},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}

